
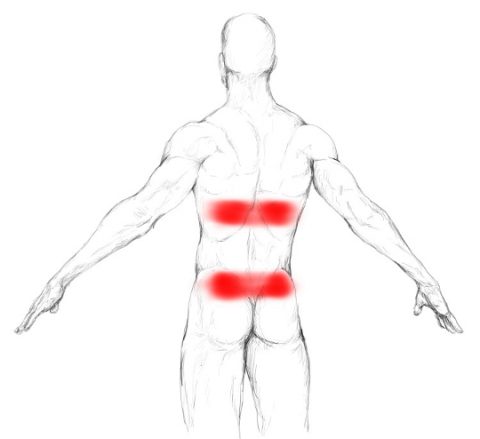
These pain patterns in muscles follow specific nerve pathways and have been readily mapped to allow for identification of the causative pain factor. When trigger points are present in muscles there is often pain and weakness in the associated structures. This crisis of energy produces sensitizing substances that interact with some nociceptive (pain) nerves traversing in the local region which in turn can produce localized pain within the muscle at the neuromuscular junction (Travell and Simons 1999). These sustained contractions of muscle sarcomeres compresses local blood supply restricting the energy needs of the local region. Indeed, the trigger point has an abnormal biochemical composition with elevated concentrations of acetylcholine, noradrenaline and serotonin and a lower pH. The integrated hypothesis theory states that trigger points form from excessive release of acetylcholine which produces sustained depolarization of muscle fibers. These in turn can pull on tendons and ligaments associated with the muscle and can cause pain deep within a joint where there are no muscles. They form as a local contraction in a small number of muscle fibers in a larger muscle or muscle bundle. Goldfinch)Īctivation of trigger points may be caused by a number of factors, including acute or chronic muscle overload, activation by other trigger points (key/satellite, primary/secondary), disease, psychological distress (via systemic inflammation), homeostatic imbalances, direct trauma to the region, collision trauma (such as a car crash which stresses many muscles and causes instant trigger points), radiculopathy, infections and health issues such as smoking. Patients can have a trigger point in their upper trapezius and when compressed feel pain in their forearm, hand and fingers (S. Palpation of the trigger point reproduces the patient's complaint of pain, and the pain radiates in a distribution of the muscle and/or nerve.The painful point can be felt as a nodule or band in the muscle, and a twitch response can be elicited on stimulation of the trigger point.Pain related to a discrete, irritable point in skeletal muscle or fascia, not caused by acute local trauma, inflammation, degeneration, neoplasm or infection.Janet Travell to describe a clinical finding with the following characteristics: The term "trigger point" was coined in 1942 by Dr.

Other health professionals, such as athletic trainers, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, acupuncturists, massage therapists and structural integrators are also aware of these ideas and many of them make use of trigger points in their clinical work as well. Osteopathic as well as chiropractic schools also include trigger points in their training. These include physiatrists (physicians specializing in physical medicine and rehabilitation), family medicine, and orthopedics. This is because a muscle spasm refers to the entire muscle contracting whereas the local twitch response also refers to the entire muscle but only involves a small twitch, no contraction.Īmong physicians, various specialists might use trigger point therapy. The local twitch response is not the same as a muscle spasm. Ĭompression of a trigger point may elicit local tenderness, referred pain, or local twitch response. There is variation in the methodology for diagnosis of trigger points and a dearth of theory to explain how they arise and why they produce specific patterns of referred pain. Practitioners claim to have identified reliable referred pain patterns which associate pain in one location with trigger points elsewhere. The trigger point model states that unexplained pain frequently radiates from these points of local tenderness to broader areas, sometimes distant from the trigger point itself. Nonetheless, the concept of trigger points provides a framework which may be used to help address certain musculoskeletal pain. Accordingly, a formal acceptance of myofascial " knots" as an identifiable source of pain is more common among bodyworkers, physical therapists, chiropractors, and osteopathic practitioners. They are a topic of ongoing controversy, as there is limited data to inform a scientific understanding of the phenomenon. They are associated with palpable nodules in taut bands of muscle fibers. Myofascial trigger points ( MTrPs), also known as trigger points, are described as hyperirritable spots in the skeletal muscle.
Medical condition Myofascial trigger point


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
